|
Ivan BeschastnikhPronouns: he/himAssociate Professor Systopia lab, SPL lab Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia bestchai@cs.ubc.ca, ICICS 327 My free/busy calendar |
Prospective students: please see this page.
About me
I have broad research interests that usually touch on systems and software engineering. My current projects span distributed systems, formal methods, networks, privacy, and machine learning. I enjoy building and studying real software systems and tend to be empirical in my research. You can find links to most of the software generated as part of my research on this site.
In the Computer Science department, I am part of both Systopia lab and Software Practices Lab (SPL). I am also part of several other groups across UBC:
- Data Science Institute (DSI)
- Blockchain@UBC
- Designing for People (DFP) Research Cluster
- UBC ICICS Centre for AI Decision-making and Action (CAIDA)
I started at UBC in 2013. Before UBC I was working on my PhD at the University of Washington in Seattle. At UW I worked with Tom Anderson, Michael Ernst, and Arvind Krishnamurthy on tools to infer models of complex systems from logs of their behavior, networked testbeds, DHTs, and other fun topics. Prior to UW, I was an undergraduate at the University of Chicago, where I was introduced to research by Pete Beckman.
Here are some recent(ish) talks/interviews/etc:
- Emilie gave a great talk on our FSE 2024 paper on mining/interpreting Issue-PR graphs in GitHub at the Open Source Summit. April 2024.
- Released a co-authored CIFAR AI Insights policy document on Federated Data Access, Towards a Proportionate and Risk-Based Approach to Federated Data Access in Canada. August 2023
- Compiling Distributed System Models Into Implementations with PGo, talk by Finn and Shayan on PGo, presented in the AWS Automated Reasoning Group, February 2022.
- Successfully Publishing your Research (Think about peer review, frequently!), talk at EuroSys Shadow PC meeting, February 2020.
- Compiling Distributed System Models into Implementations with PGo, talk at TLA+ Conference, September 2019.
- Deep Dive Into Erlay and Biscotti, Advance tech podcast, July 2019.
- Comparing Software Repositories Visually with RepoGrams, talk at Visualization Across UBC, April 2019.
- Private and secure distributed ML, FoolsGold and Biscotti (BlockML) projects, 2018.
- Program analysis for distributed systems, Dinv, Dara, and PGo projects, 2018.
- Scalable Constraint-based Virtual Data Center Allocation, talk at UC Louvain, August 2016.
- Mining temporal and data-temporal specifications, Texada and Quarry projects, August 2016.
- Helping developers make sense of distributed systems, Colloquium at Sonoma U., October 2015.
- Making sense of distributed systems, UBC CS FLS talk, January 2014.
- Modeling systems from logs of their behavior, Microsoft Research Redmond, July 2013.
Here is my research statement (for my tenure review) from 2018 that summarizes my work at UBC from 2013-2018.
If you intend to apply for academic jobs in CS, you may want to see my research and teaching statements (from 2013).
You can also find my profiles on Google Scholar and DBLP.
Research projects
Recent areas of focus:
- Using formal methods in systems, particularly distributed systems
- Developing novel SE tools to support systems developers
- Program analysis, specifically specification mining
- New data center designs (e.g., resource disaggregation)
- Private and secure distributed multi-party ML
- Physical insider attacks and defences
Research projects sampler:
|
|
PGo: source to source compiler from Modular PlusCal into Go lang. PGo compiles Modular PlusCal formal specifications into Go implementations. PGo is designed to reduce the developer burden of implementing a correct distributed system specification, and increases developers' confidence in the correctness of their implementations. Watch a video in which Finn and Shayan detail PGo. |
|
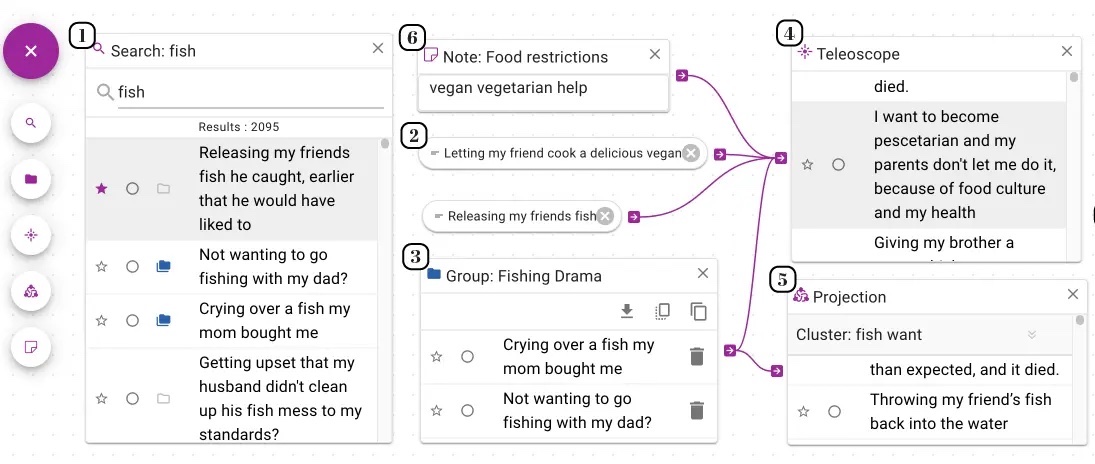
Teleoscope: a system for exploring large document sets by building machine learning workflows Teleoscope (from teleology and telescope) helps to discover purpose and meaning. The system is designed with qualitative researchers in mind, but can be used by anyone interested in exploring themes in a large dataset. The tool is publicly deployed. You can also watch a video that overviews the tool. |
|
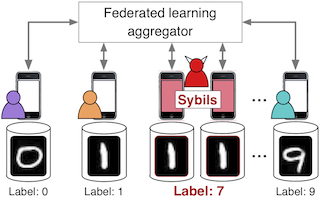
Private and secure distributed machine learning (ML) To train multi-party ML models from user-generated data, users must provide and share their training data, which can be expensive or privacy-violating. We are exploring ways to augment state-of-the-art approaches, like federated learning, with better security/privacy (e.g., defences to sybil-based poisoning). And, we are developing brand-new distributed ML approaches that do away with centralization. |
|
LEAP: intersection of health, ML, privacy, ethics, and security We've teamed up with a group of researchers interested in topics at the intersections of health, machine learning, privacy, ethics, and security. We aspire to build usable privacy-enhancing systems that can be readily deployed in healthcare domains. We pursue a variety of projects and collaborations in different domains. |
|
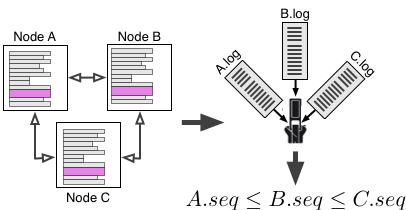
Dinv: distributed system state invariant detector. (Video!) Distributed systems are difficult to debug and understand. One reasons for this is distributed state, which is not easily accessible and must be pieced together from the states of the individual nodes. Dinv statically analyzes the node source code to identify distributed state variables and then instruments the system to record these variables at runtime. After system execution Dinv uses dynamic analysis to determine consistent distributed state snapshots and infers likely distributed state invariants. |
|
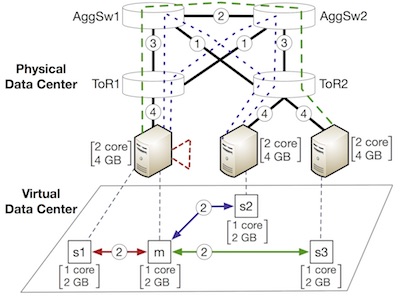
NetSolver: Scalable Virtual Data Center Allocation NetSolver is an SMT-based VDC allocation tool for multi-path VDC allocation with end-to-end bandwidth guarantees. It scales to data centers with 1,000 or more servers, and can make allocations quickly enough to be applied in practice, while simultaneously improving data center utilization relative to previous work. |
|
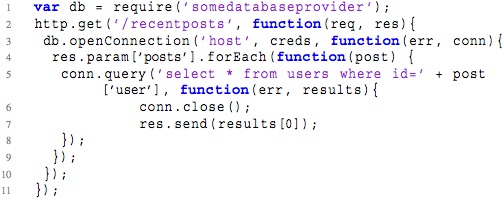
Callbacks are a popular language features in JavaScript. However, they are also a source of comprehension and maintainability issues. The example on the left illustrates nested, anonymous callbacks, as well as asynchronous callback scheduling. Not much code, but so much complexity! We carried out a study of callbacks across 138 applications, and are developing tools to help developers manage callback hell in their applications. Our analysis code from the study is online. |
|
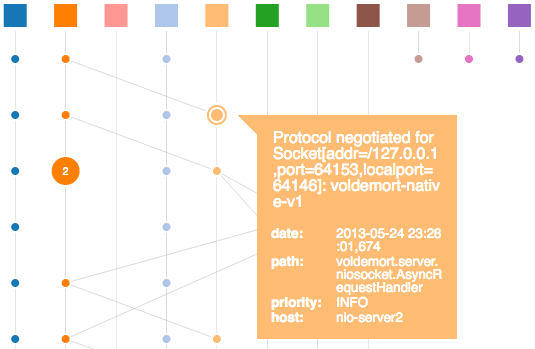
ShiViz and TSViz: Visualizing distributed/multi-threaded system logs. (Try ShiViz, Try TSViz) Concurrent systems generate logs that are complex and unwieldy. ShiViz helps developers understand distributed system logs through visualization. ShiViz visualizes a distributed execution that has been instrumented to record vector clock timestamps (e.g., with distributed clock instrumentation library). The visualizations are simple-to-understand and interactive. The user can understand complex system behavior by exploring the log through the visualization, comparing executions side-by-side, searching for specific behavior (by keyword and topology), and much more. TSViz, builds on ShiViz and visualizes multi-threaded logs with vector clocks and physical timestamps. |
|
Repograms: exploring and juxtaposing software repositories. Repograms is a tool for visualizing the activity in a software repositories (e.g., git). It uses a simple metaphor of multi-coloured blocks of varying sizes to encode different kinds of information about the repository. For example, each unique committer could be assigned to a colour and the sequence of blocks can reveal who works when, and how many commits each person makes. |
|
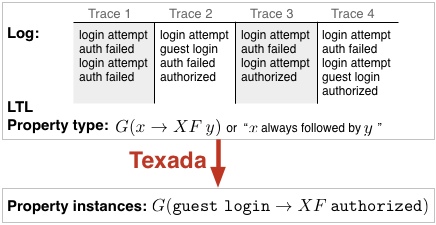
Texada: general LTL specification mining. (video) Texada is a temporal specification mining tool for extracting linear temporal logic (LTL) specifications of arbitrary length and complexity. Texada takes a user-defined LTL property type template and a log of program traces as input and outputs a set of instantiations of the property type (i.e., LTL formulas) that are true on the traces in the log. Texada is envisioned as a specification mining engine on top of which new software analyses can be developed. |
|
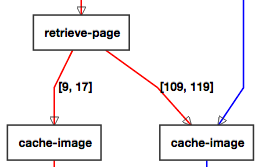
Perfume: Inferring performance models. (video) Perfume summarizes a system's logged executions in a performance-aware, behavioural model. Performance metrics present in logs convey vital information about most systems, yet previous model inference work ignores performance data. By leveraging this information, Perfume generates more precise models, which can help developers understand system behavior that depends on metrics like execution time, network traffic, or energy consumption. |
|
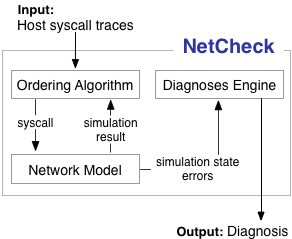
NetCheck: Diagnosing networked applications from blackbox traces. Networked applications can fail for many complex reasons having to do with the network or mis-behavior of a remote end-host. NetCheck uses traces of syscalls calls made by the application and any end-hosts that are pertinent to the application logic (e.g., the user's desktop, an SMTP server, and a DHCP server). Using these traces NetCheck reconstructs a plausible partial order of network communication without any clock synchronization. It then uses a set of rules to diagnose network issues that are apparent in the reconstructed network behavior. |
|
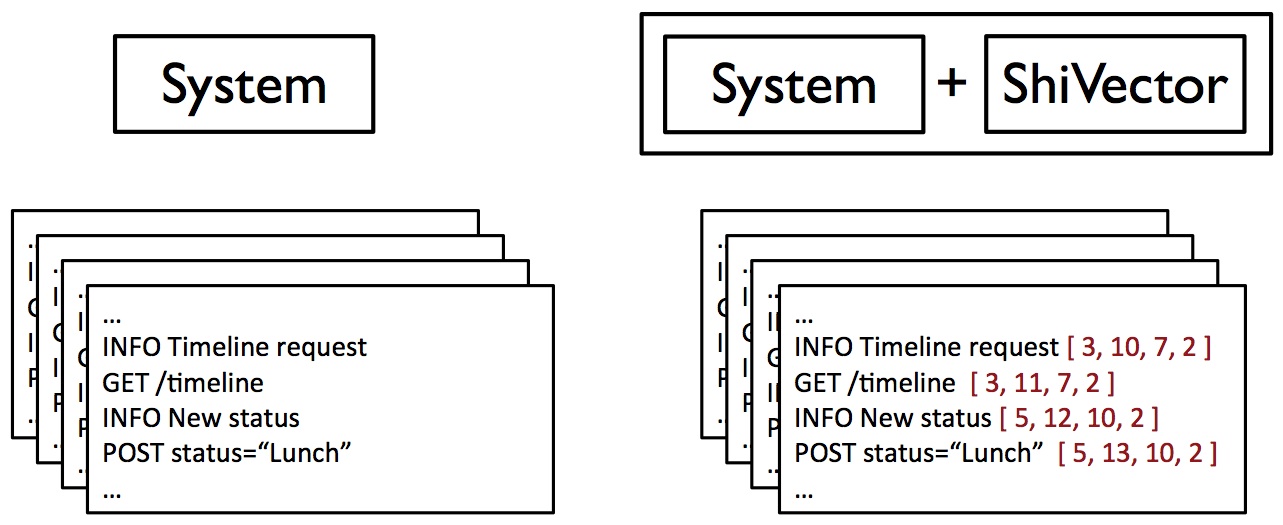
Distributed clocks: Augmenting logs of distributed systems with vector clocks. A major challenge in debugging distributed systems is analyzing execution logs generated at multiple hosts. The distribute clock libraries transparently add vector timestamps to logs generated by a distributed system in several different programming languages. These vector-timestamped logs capture partial ordering information, which can be used for further analysis and log comprehension. The resulting logs can be visualized with ShiViz. |
|
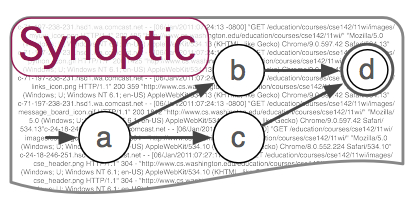
Synoptic: Inferring FSM models from logs of sequential executions. Systems are often difficult to debug and to understand. A typical way of gaining insight into system behavior is by inspecting execution logs. Manual inspection of logs, however, is an arduous process. This project helps this problem by designing Synoptic, a tool to produce summary model of a system log. Two features distinguish Synoptic from other tools. First, Synoptic's models preserve key invariants mined from the log, making them more accurate. Second, Synoptic uses refinement to derive the model, which is more efficient than traditional coarsening algorithms. |
|
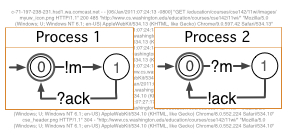
CSight: Inferring communicating FSM models of distributed systems. CSight mines a communicating FSM model to represent the distributed system that generated a set of logs. Like Synoptic, CSight mines models that preserve temporal properties of the system. Engineers can use the inferred models to understand complex behavior, detect anomalies, debug, and increase confidence in the correctness of their implementations. |
|
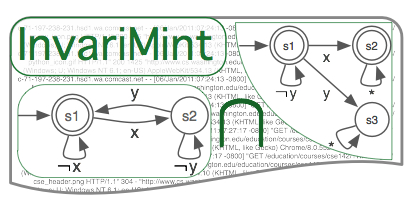
InvariMint: Declaratively specifying model inference algorithms. InvariMint is an approach to express FSM model inference algorithms in a common framework. The key idea is to encode properties of an algorithms as finite state machines. These properties can then be instantiated for a specific input log of observations and combined to generate/infer a model that describes the observations. InvariMint (1) leads to new fundamental insights and better understanding of existing algorithms, (2) simplifies creation of new algorithms, including hybrids that extend existing algorithms, and (3) makes it easy to compare and contrast previously published algorithms. |
(Show) Older projects
(Show) Even older projects
Research publications
Pre-prints on Arxiv | Peer-reviewed publications by year: | |
2025 | |
|
TraceLinking Implementations with their Verified Designs Finn Hackett, Ivan Beschastnikh,. To appear in OOPSLA 2025. | |
|
Orthrus: Accelerating Multi-BFT Consensus through Concurrent Partial Ordering of Transactions Hanzheng Lyu, Shaokang Xie, Jianyu Niu, Ivan Beschastnikh, Yinqian Zhang, Mohammad Sadoghi, Chen Feng. ICDE 2025. | |
|
Ladon: High-Performance Multi-BFT Consensus via Dynamic Global Ordering Hanzheng Lyu, Shaokang Xie, Jianyu Niu, Chen Feng, Yinqian Zhang, Ivan Beschastnikh. EuroSys 2025. | |
|
pdf slides implementation |
FedFetch: Faster Federated Learning with Adaptive Downstream Prefetching Qifan Yan, Andrew Liu, Shiqi He, Mathias Lécuyer, Ivan Beschastnikh. INFOCOM 2025. |
|
pdf implementation |
Listening to the Firehose: Sonifying Z3’s Behavior Finn Hackett, Ivan Beschastnikh. ICSE 2025, NIER track. |
|
pdf |
Promises and perils of using Transformer-based models for SE research. Yan Xiao, Xinyue Zuo, Xiaoyue Lu, Jin Song Dong, Xiaochun Cao, Ivan Beschastnikh. Neural Networks, vol 184, 2025. |
2024 | |
|
pdf slides video |
Making Sense of Multi-Threaded Application Performance at Scale with NonSequitur Augustine Wong, Paul Bucci, Ivan Beschastnikh Alexandra Fedorova. OOPSLA 2024. |
|
pdf,
video blog supplementary pdf implementation |
Revealing Software Development Work Patterns with PR-Issue Graph Topologies Cleidson de Souza, Emilie Ma, Jesse Wong, Dongwook Yoon, Ivan Beschastnikh. FSE 2024. |
|
pdf article |
The Fine Balance Between Helping With Your Job And Taking It: AI Code Assistants Come To The Fore Cleidson de Souza, Gema Rodríguez-Pérez, Manaal Basha, Dongwook Yoon, Ivan Beschastnikh. IEEE Sofware. |
2023 | |
|
pdf implementation |
Compiling Distributed System Models with PGo Finn Hackett, Shayan Hosseini, Renato Costa, Matthew Do, Ivan Beschastnikh. ASPLOS 2023. Distinguished Artifact Award |
|
pdf implementation |
GlueFL: Reconciling Client Sampling and Model Masking for Bandwidth Efficient Federated Learning Shiqi He, Qifan Yan, Feijie Wu, Lanjun Wang, Mathias Lécuyer, Ivan Beschastnikh. MLSys 2023. |
|
pdf implementation |
Scaling Blockchain Consensus via a Robust Shared Mempool Fangyu Gai, Jianyu Niu, Ivan Beschastnikh, Chen Feng, Sheng Wang. ICDE 2023. |
|
pdf implementation |
Mercury: Fast Transaction Broadcast in High Performance Blockchain Systems Mingxun Zhou, Yilin Han, Liyi Zeng, Peilun Li, Fan Long, Dong Zhou, Ivan Beschastnikh, Ming Wu. INFOCOM 2023. |
|
pdf |
Auto-tuning Elastic Applications in Production Adalberto R. Sampaio Junior, Ivan Beschastnikh, Daryl Maier, Don Bourne, Vijay Sundaresan. ICSE 2023, SEIP track. |
|
pdf implementation |
XSnare: Application-specific client-side cross-site scripting protection Jose Carlos Pazos, Jean-Sébastien Légaré, Ivan Beschastnikh. Empirical Software Engineering Journal (EMSE) 2023. |
|
pdf |
Affective robots need therapy Paul Bucci, David Marino, Ivan Beschastnikh. ACM Transactions on Human-Robot Interaction (THRI), 2023. |
2022 | |
|
pdf slides dataset |
CoSpot: A Cooperative VM Allocation Framework for Increased Revenue from Spot Instances Syed M. Iqbal, Haley Li, Shane Bergsma, Ivan Beschastnikh, Alan J. Hu. SoCC 2022. |
|
pdf implementation |
Repairing Failure-inducing Inputs with Input Reflection Yan Xiao, Yun Lin, Ivan Beschastnikh, Changsheng Sun, David S. Rosenblum, Jin Song Dong. ASE 2022. |
|
pdf implementation |
Self-Checking Deep Neural Networks for Anomalies and Adversaries in Deployment Yan Xiao, Ivan Beschastnikh, Yun Lin, Rajdeep Singh Hundal, Xiaofei Xie, David S. Rosenblum, Jin Song Dong. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing (TDSC), 2022. |
|
pdf implementation video |
Linear-time Temporal Logic guided Greybox Fuzzing Ruijie Meng, Zhen Dong, Jialin Li, Ivan Beschastnikh, Abhik Roychoudhury. ICSE 2022. |
|
pdf arxiv implementation video |
One Bad Apple Spoils the Bunch: Transaction DoS in MimbleWimble Blockchains Seyed Ali Tabatabaee, Charlene Nicer, Ivan Beschastnikh, Chen Feng. ICBC 2022. |
|
pdf implementation |
Fair Decision Making via Automated Repair of Decision Trees Zhang Jiang, Ivan Beschastnikh, Sergey Mechtaev, Abhik Roychoudhury. Fairware workshop at ICSE 2022. |
2021 | |
|
pdf data/scripts |
"@alex, this fixes #9": Analysis of Referencing Patterns in Pull Request Discussions Ashish Chopra, Morgan Mo, Samuel Dodson, Ivan Beschastnikh, Sidney Fels, Dongwook Yoon. CSCW 2021. Awarded an Impact Recognition |
|
pdf slides |
Jumpgate: Automating Integration of Network Connected Accelerators Craig Mustard, Swati Goswami, Niloofar Gharavi, Joel Nider, Ivan Beschastnikh, Alexandra (Sasha) Fedorova. SYSTOR 2021. |
|
pdf slides video implementation |
Dissecting the Performance of Chained-BFT Fangyu Gai, Ali Farahbakhsh, Jianyu Niu, Chen Feng, Ivan Beschastnikh, Hao Duan. ICDCS 2021. |
|
pdf video implementation |
Self-Checking Deep Neural Networks in Deployment Yan Xiao, Ivan Beschastnikh, David S. Rosenblum, Changsheng Sun, Sebastian Elbaum, Yun Lin, Jin Song Dong. ICSE 2021. |
|
pdf arxiv implementation |
XSnare: Application-specific client-side cross-site scripting protection Jose Carlos Pazos, Jean-Sébastien Légaré, Ivan Beschastnikh. SANER 2021. |
|
chapter pdf book |
Blockchain Governance: De Facto (x)or Designed? Darra Hofman, Quinn DuPont, Angela Walch, Ivan Beschastnikh. Chapter in Lemieux V.L., Feng C. (eds) Building Decentralized Trust. Springer, Cham. |
2020 | |
|
pdf implementation arxiv |
Biscotti: A Blockchain System for Private and Secure Federated Learning Muhammad Shayan, Clement Fung, Chris J.M. Yoon, Ivan Beschastnikh. Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems (IEEE TPDS) Special Section on AI/ML/DL 2020. |
|
pdf video implementation arxiv |
Parking Packet Payload with P4 Swati Goswami, Nodir Kodirov, Craig Mustard, Ivan Beschastnikh, Margo Seltzer. CoNEXT 2020 |
|
pdf video, slides arxiv implementation |
The Limitations of Federated Learning in Sybil Settings Clement Fung, Chris J.M. Yoon, Ivan Beschastnikh. RAID 2020 |
|
pdf slides video ShiViz tool |
Visualizing Distributed System Executions Ivan Beschastnikh, Perry Liu, Albert Xing, Patty Wang, Yuriy Brun, Michael D. Ernst. ACM Transactions on Software Engineering and Methodology (TOSEM) 2020. Presented at ICSE 2020 Journal First track. |
|
pdf materials |
Scalable Constraint-based Virtual Data Center Allocation. Samuel Bayless, Nodir Kodirov, Syed M. Iqbal, Ivan Beschastnikh, Holger Hoos, Alan Hu. Artificial Intelligence Journal (AIJ), January 2020. |
2019 | |
|
pdf arxiv BIP 330 |
Erlay: Efficient Transaction Relay for Bitcoin Gleb Naumenko, Gregory Maxwell, Pieter Wuille, Alexandra (Sasha) Fedorova, Ivan Beschastnikh. CCS 2019. [Bitcoin Improvement Proposals 330.] |
|
pdf,
slides extended pdf arxiv implementation |
Brokered Agreements in Multi-Party Machine Learning Clement Fung, Ivan Beschastnikh. APSys 2019 |
|
Learning to Listen for Design Elisa Baniassad, Ivan Beschastnikh, Reid Holmes, Gregor Kiczales, Meghan Allen. SPLASH 2019 Onward! Essays | |
|
pdf slides |
Jumpgate: In-Network Processing as a Service for Data Analytics Craig Mustard, Fabian Ruffy, Anny Gakhokidze, Ivan Beschastnikh, Alexandra (Sasha) Fedorova. HotCloud 2019 |
|
pdf implementation |
Improving Microservice-based Applications with Runtime Placement Adaptation Adalberto R. Sampaio Junior, Julia Rubin, Ivan Beschastnikh, Nelson Rosa. Journal of Internet Services and Applications (JISA) |
|
pdf slides materials |
Vulnerability & Blame: Making Sense of Unauthorized Access to Smartphones Diogo Marques, Tiago Guerreiro, Luis Carriço, Ivan Beschastnikh Konstantin Beznosov. CHI 2019 |
|
pdf slides materials |
Mining Specifications from Documentation Using a Crowd Peng Sun, Chris Brown, Ivan Beschastnikh, Kathryn Stolee. SANER 2019 |
2018 | |
|
pdf slides implementation |
Iroko: A Framework to Prototype Reinforcement Learning for Data Center Traffic Control Fabian Ruffy, Michael Przystupa, Ivan Beschastnikh. Workshop on ML for Systems at NIPS 2018. |
|
pdf |
Performance Comprehension at WiredTiger Alexandra (Sasha) Fedorova, Craig Mustard, Ivan Beschastnikh, Julia Rubin, Augustine Wong, Svetozar Miucin, Louis Ye FSE 2018 |
|
pdf slides |
VNF Chain Allocation and Management at Data Center Scale Nodir Kodirov, Samuel Bayless, Fabian Ruffy, Ivan Beschastnikh, Holger Hoos, Alan Hu. ANCS 2018 |
|
pdf slides video implementation |
Inferring and Asserting Distributed System Invariants Stewart Grant, Hendrik Cech, Ivan Beschastnikh. ICSE 2018 |
|
Tsumiki: A Meta-Platform for Building Your Own Testbed Justin Cappos, Yanyan Zhuang, Albert Rafetseder, Ivan Beschastnikh. Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems (TPDS). | |
|
pdf slides |
Non-Stranger Danger: Examining the Effectiveness of Smartphone Locks in Preventing Intrusions by Socially-Close Adversaries Diogo Marques, Tiago Guerreiro, Luis Carriço, Ivan Beschastnikh Konstantin Beznosov WAY 2018 workshop, co-located with SOUPS 2018. |
2017 | |
|
pdf slides extended slides |
Tolerating Faults in Disaggregated Datacenters
Amanda Carbonari, Ivan Beschastnikh. HotNets 2017 |
|
pdf implementation |
Scalable and Fault Tolerant Platform for Distributed Learning on Private Medical Data
Alborz Amir-Khalili, Soheil Kianzad, Rafeef Abugharbieh, Ivan Beschastnikh. MICCAI MLMI 2017 |
|
pdf slides poster |
Supporting Microservice Evolution Adalberto R. Sampaio Junior, Harshavardhan Kadiyala, Bo Hu, John Steinbacher, Antony W. Erwin, Nelson Rosa, Ivan Beschastnikh, Julia Rubin. ICSME 2017, NIER track. |
|
pdf slides implementation study site |
Refactoring Asynchrony in JavaScript Keheliya Gallaba, Quinn Hanam, Ali Mesbah, Ivan Beschastnikh. ICSME 2017 |
|
pdf |
Scalable Constraint-based Virtual Data Center Allocation Samuel Bayless, Nodir Kodirov, Ivan Beschastnikh, Holger Hoos, Alan Hu. IJCAI 2017 |
|
pdf slides |
Accelerating software engineering research adoption with Analysis Bots Ivan Beschastnikh, Mircea F. Lungu, Yanyan Zhuang. ICSE 2017, NIER track. |
|
pdf slides implementation video |
Studying multi-threaded behavior with TSViz Matheus Nunes, Harjeet Lalh, Ashaya Sharma, Augustine Wong, Svetozar Miucin, Alexandra (Sasha) Fedorova, Ivan Beschastnikh. ICSE 2017, Tool demonstration. |
|
pdf slides study site |
Characterizing Social Insider Attacks on Facebook Wali Usmani, Diogo Marques, Ivan Beschastnikh, Konstantin Beznosov, Tiago Guerreiro, Luis Carriço. CHI 2017 |
2016 | |
|
pdf implementation |
Visually Reasoning about System and Resource Behavior Tony Ohmann, Ryan Stanley, Ivan Beschastnikh, Yuriy Brun. ICSE 2016, Tool demonstration. |
|
CACM pdf Queue pdf implementation |
Debugging Distributed Systems: Challenges and options for validation and debugging Ivan Beschastnikh, Patty Wang, Yuriy Brun, Michael D. Ernst. Communications of the ACM, vol. 59, no. 8, Aug. 2016, pp. 32-37. ACM Queue, vol. 14, no. 2, March/April 2016, pp. 91-110. |
|
pdf slides implementation demo1.json, demo2.json |
Comparing Repositories Visually with RepoGrams Daniel Rozenberg, Ivan Beschastnikh, Fabian Kosmale, Valerie Poser, Heiko Becker, Marc Palyart, Gail Murphy. MSR 2016 |
2015 | |
|
poster abstract implementation |
Inferring likely data invariants of distributed systems Stewart Grant Sam Creed, Ivan Beschastnikh. Poster at SOSP 2015. |
|
pdf slides video implementation |
General LTL Specification Mining Caroline Lemieux, Dennis Park, Ivan Beschastnikh. ASE 2015 |
|
pdf slides models |
Synergizing Specification Miners through Model Fissions and Fusions Tien-Duy B. Le, Xuan-Bach D. Le, David Lo, Ivan Beschastnikh. ASE 2015 |
|
pdf video implementation |
Investigating Program Behavior Using the Texada LTL Specifications Miner Caroline Lemieux, Ivan Beschastnikh. ASE 2015, Tool demonstration. |
|
pdf slides implementation dataset |
Don't Call Us, We'll Call You: Characterizing Callbacks in JavaScript Keheliya Gallaba, Ali Mesbah, Ivan Beschastnikh. ESEM 2015 Best Full Paper Award |
|
pdf |
Using declarative specification to improve the understanding,
extensibility, and comparison of model-inference algorithms Ivan Beschastnikh, Yuriy Brun, Jenny Abrahamson, Michael D. Ernst, Arvind Krishnamurthy. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering (TSE), in press, 21 pages, April 2015. (Extended version of the ICSE 2013 paper). |
2014 | |
|
pdf slides implementation |
Templated Visualization of Object State with Vebugger Daniel Rozenberg, Ivan Beschastnikh. VISSOFT'14, NIER track. |
|
pdf slides supplementary info |
Behavioral Resource-Aware Model Inference Tony Ohmann, Michael Herzberg, Sebastian Fiss, Armand Halbert, Marc Palyart, Ivan Beschastnikh, Yuriy Brun. ASE 2014 |
|
pdf slides |
Inferring Models of Concurrent Systems from Logs of their Behavior with CSight Ivan Beschastnikh, Yuriy Brun, Michael D. Ernst, Arvind Krishnamurthy. ICSE 2014 |
|
poster abstract |
Shedding Light on Distributed System Executions Jenny Abrahamson, Ivan Beschastnikh, Yuriy Brun, Michael D. Ernst. Poster at ICSE 2014 |
|
pdf, tr poster slides |
NetCheck: Network Diagnoses from Blackbox Traces Yanyan Zhuang, Eleni Gessiou, Steven Portzer, Fraida Fund, Monzur Muhammad, Ivan Beschastnikh, Justin Cappos. NSDI 2014 |
|
pdf slides |
Mining Precise Performance-Aware Behavioral Models from Existing Instrumentation Tony Ohmann, Kevin Thai, Ivan Beschastnikh Yuriy Brun. ICSE 2014, NIER track. |
|
Inferring Models of Concurrent Systems from Logs of their Behavior with CSight Ivan Beschastnikh, Yuriy Brun, Michael D. Ernst, Arvind Krishnamurthy. UBC, Department of Computer Science, Technical Report, 2014-02-28. | |
2013 | |
|
pdf slides |
Unifying FSM-inference Algorithms through Declarative Specification Ivan Beschastnikh, Yuriy Brun, Jenny Abrahamson, Michael D. Ernst, Arvind Krishnamurthy. ICSE 2013 (Extended version published as a TSE 2015 journal paper). |
| pdf slides |
Understanding Regression Failures through Test-Passing and Test-Failing Code Changes Roykrong Sukkerd, Ivan Beschastnikh, Jochen Wuttke, Sai Zhang, Yuriy Brun. ICSE 2013, NIER track. |
|
NetCheck Test Cases: Input Traces and NetCheck Output Yanyan Zhuang, Ivan Beschastnikh Justin Cappos. NYU Poly, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Report TR-CSE-2013-03, 10/29/2013. | |
|
Unifying FSM-inference Algorithms through Declarative Specification Ivan Beschastnikh, Yuriy Brun, Jenny Abrahamson, Michael D. Ernst, Arvind Krishnamurthy. University of Washington CSE technical report UW-CSE-13-03-01, March 2013. | |
2012 | |
|
Effects of Centralized and Distributed Version Control on Commit Granularity Jochen Wuttke, Ivan Beschastnikh, Yuriy Brun Published in TinyToCS vol. 1, 2012. | |
| pdf
slides |
Inferring Networked System Models from Behavior Traces Ivan Beschastnikh Student Workshop at CoNEXT 2012. |
|
Sonora: A Platform for Continuous Mobile-Cloud Computing Fan Yang, Zhengping Qian, Xiuwei Chen, Ivan Beschastnikh, Li Zhuang, Lidong Zhou, Guobin Shen. Microsoft Research technical report MSR-TR-2012-34, March 2012. | |
2011 | |
| pdf tr slides |
Scalable Consistency in Scatter Lisa Glendenning, Ivan Beschastnikh, Arvind Krishnamurthy, Tom Anderson. SOSP 2011 |
| pdf
slides teaser video |
Leveraging Existing Instrumentation to Automatically Infer Invariant-Constrained Models Ivan Beschastnikh, Yuriy Brun, Sigurd Schneider, Michael Sloan, Michael D. Ernst. ESEC/FSE 2011 |
|
Synoptic: Studying Logged Behavior with Inferred Models Ivan Beschastnikh, Jenny Abrahamson, Yuriy Brun, Michael D. Ernst. ESEC/FSE 2011, Tool demonstration. | |
| pdf
slides |
Mining Temporal Invariants from Partially Ordered Logs Ivan Beschastnikh, Yuriy Brun, Michael D. Ernst, Arvind Krishnamurthy, Tom Anderson. ACM SIGOPS Operating Systems Review, vol. 45, no. 3, December 2011, pp. 39–46. Initially appeared at SLAML 2011. |
| pdf
slides |
Bandsaw: Log-powered test scenario generation for distributed systems Ivan Beschastnikh, Yuriy Brun, Michael D. Ernst, Arvind Krishnamurthy, Tom Anderson. Work in Progress at SOSP 2011. |
2010 | |
|
Retaining Sandbox Containment Despite Bugs in Privileged Memory-Safe Code Justin Cappos, Armon Dadgar, Jeffrey Rasley, Justin Samuel, Ivan Beschastnikh, Cosmin Barsan, Arvind Krishnamurthy, Tom Anderson. CCS 2010 | |
| pdf
slides |
Synoptic: Summarizing system logs with refinement Sigurd Schneider, Ivan Beschastnikh, Slava Chernyak, Michael D. Ernst, Yuriy Brun. Workshop on Managing Systems via Log Analysis and Machine Learning Techniques, SLAML 2010. |
|
Self-Presentation: Structured and semi-structured user profiles Linda Le, Ivan Beschastnikh, David W. McDonald. Studying Online Behaviour Workshop at CHI 2010. | |
| poster |
MiST: A Platform for Mobile-Cloud Computing in Streams Fan Yang, Zhengping Qian, Ivan Beschastnikh, Li Zhuang, Mao Yang, Amre Shakimov, Guobin Shen, Lidong Zhou. Poster at Microsoft Research Mobile + Cloud Summit, Redmond, 2010. |
2009 | |
| www |
Teaching networking and distributed systems with Seattle Justin Cappos, Ivan Beschastnikh. Journal of Computing Sciences in Colleges. Volume 25 Issue 1, October 2009. |
|
Seattle: The Internet as an Educational Testbed Justin Cappos, Ivan Beschastnikh, Arvind Krishnamurthy, Tom Anderson. SIGCSE 2009 | |
|
Promoting Quality in Wikipedia through Enculturation Ivan Beschastnikh, David W. McDonald, Mark Zachry, Travis Kriplean, Alan Borning. Approaching 'Amateur' Workshop at GROUP 2009. | |
|
System Design for Social Translucence in Socially Mediating Technologies David W. McDonald, Ivan Beschastnikh, Travis Kriplean, Alan Borning, Mark Zachry. Socially Mediating Technologies Workshop at CHI 2009. | |
|
Designing Mediating Spaces Between Citizens and Government Travis Kriplean, Ivan Beschastnikh, Alan Borning, David W. McDonald, Mark Zachry. Socially Mediating Technologies Workshop at CHI 2009. | |
2008 | |
| pdf
slides |
SatelliteLab: Adding Heterogeneity to Planetary-Scale Testbeds Marcel Dischinger, Andreas Haeberlen, Ivan Beschastnikh, Krishna P. Gummadi, Stefan Saroiu. SIGCOMM 2008 |
| pdf slides |
Articulations of WikiWork: Uncovering Valued Work in Wikipedia through Barnstars Travis Kriplean, Ivan Beschastnikh, David W. McDonald. CSCW 2008 Best Paper Honorable Mention |
| pdf slides |
Wikipedian Self-Governance in Action: Motivating the Policy Lens Ivan Beschastnikh, Travis Kriplean, David W. McDonald. ICWSM 2008 ICWSM 2018 10-Year Test of Time honorable mention Best Paper Award |
2007 | |
| pdf slides |
Community, Consensus, Coercion, Control: CS*W or How Policy Mediates Mass Participation Travis Kriplean, Ivan Beschastnikh, David W. McDonald, Scott Golder. GROUP 2007 |
|
Building an Infrastructure for Urgent Computing Pete Beckman, Ivan Beschastnikh, Suman Nadella, Nick Trebon. Chapter in 'High Performance Computing and Grids in Action' by IOS Press, Amsterdam, 2007 | |
2006 | |
|
SPRUCE: A System for Supporting Urgent High-Performance Computing Pete Beckman, Suman Nadella, Nick Trebon, Ivan Beschastnikh IFIP WoCo9, 2006. | |
| www |
VFER: High-performance Transport in User Space Stanislav Shalunov, Ivan Beschastnikh SuperComputing 2006 Bandwidth Challenge Finalist, November 2006. |
2005 | |
|
The Earth Vision Time Machine: A Design for the Collaborative Sharing of Wireless Sensor Data Pete Beckman, Ivan Beschastnikh, Cameron Cooper, Isaac Wasileski Workshop on Advanced Collaborative Environments, WACE 2005 | |
Presentations
|
Seattle: A Python-based Platform for Easy Development and Deployment of Networked Systems and Applications Ivan Beschastnikh, Justin Samuel, Justin Cappos, Presentation at PyCon 2010, Atlanta, GA, February 2010 | |
|
Teaching networking and distributed systems with Seattle Ivan Beschastnikh, Justin Cappos, Tutorial at CCSC Central Plains 2010 | |
|
Teaching networking and distributed systems with Seattle Justin Cappos, Ivan Beschastnikh, Tutorial at CCSC Northwest 2009 |
Unpublished Material
|
Liberating Mobile Phones from their Primary Use Case. Ivan Beschastnikh, Yuan Zhang, Zhengping Qian, Lidong Zhou. | |
|
Integration of Static Instruction Analysis with Dynamic Information Flow Tracking. Ivan Beschastnikh, Ian Post, Joshua Schwartz, Benedict Singer. | |
|
Machine Learning for Automatic Physical DBMS Tuning. Ivan Beschastnikh and Andrew Guillory. |
Research team
I am lucky to work with an amazing group of people. One of my research principles is to let my student's interests guide the research. I encourage students to pursue topics that they find personally motivating.
Graduate students:
- Finn Hackett (PhD)
- Yanze Li (PhD, co-supervised with Alex Summers)
Undergraduate students:
- Jiayin Kralik (USRA'25)
- Emilie Ma (Honors thesis'26)
Graduate student alumni:
- Paul Bucci (PhD 2024) → Teleoscope Inc. (startup founder).
- The Computation of Meaning: From Embodied Emotions to Cognitive Schemas [pdf]
- Mishaal Kazmi (MSc 2024, co-supervised with Mathias Lécuyer)
- PANORAMIA: Privacy Auditing of Machine Learning Models without Retraining [pdf]
- Shayan Hosseini (MSc 2024) → Neon
- Reconciling the Model-Implementation Duality in PGo [pdf]
- Shiqi He (MSc 2023, co-supervised with Mathias Lécuyer) → PhD at University of Michigan
- GlueFL: Reconciling Client Sampling and Model Masking for Bandwidth Efficient Federated Learning [pdf]
- Mayank Tiwary (MSc 2023, co-supervised with Thomas Pasquier) → Salesforce
- A literature review of parameter tuning within the context of big data processing frameworks [pdf]
- Faqia Iqbal (MSc 2023)
- Privacy and Conflicting Identities in the Context of Punjabi Canadians [pdf]
- Nodir Kodirov (PhD 2021, co-supervised with Alan Hu) → Huawei Research
- Datacenter Resource Scheduling for Networked Cloud Applications [pdf]
- Matheus Stolet (MSc 2021, co-supervised with Aline Talhouk) → PhD at MPI-SWS
- Large Scale Federated Analytics and DP Budget Preservation [pdf]
- Seyed Ali Tabatabaee (MSc 2021, co-supervised with Chen Feng) → PhD at UBC
- Attacking Transaction Relay in MimbleWimble Blockchains [pdf]
- Vaastav Anand (MSc 2020) → PhD at MPI-SWS
- Dara The Explorer: Coverage Based Exploration for Model Checking of Distributed Systems in Go [pdf]
- Adam Geller (MSc 2020 co-supervised with William J. Bowman) → PhD at UBC
- An Indexed Type System for Faster and Safer WebAssembly [pdf]
- Jose Carlos Pazos (MSc 2019, primary supervisor Bill Aiello) → Wolfram
- XSnare: Application-specific, Client-side Cross-site Scripting Protection [pdf]
- Muhammad Shayan (MSc 2019) → KorbitAI
- Biscotti - A Ledger for Private and Secure Peer to Peer Machine Learning [pdf]
- Puneet Mehrotra (MSc 2019) → PhD at UBC
- Cross-device Access Control with Trusted Capsules [pdf]
- Anand Jayarajan (MSc 2019, primary supervisor Sasha Fedorova) → PhD at UToronto
- Priority-based Parameter Propagation for Distributed Deep Neural Network Training [pdf]
- Renato Costa (MSc 2019)
- Compiling Distributed System Specifications into Implementations [pdf]
- Matthew (Minh) Do (MSc 2019) → Hopper
- Corresponding formal specifications with distributed systems [pdf]
- Gleb Naumenko (MSc 2019, co-supervised with Sasha Fedorova) → Chaincode Labs
- Erlay: Efficient Transaction Relay in Bitcoin [pdf]
- Fabian Ruffy (MSc 2019) → PhD at NYU
- Data-Driven Datacenter Traffic Control [pdf]
- Jodi Spacek (MSc 2019, CGSM fellowship) → Shopify
- Amanda Carbonari (MSc 2018) → Google
- Inter-processor Communication in Disaggregated Datacenters [pdf]
- Clement Fung (MSc 2018) → PhD at CMU
- Dancing in the Dark: Private Multi-Party Machine Learning in an Untrusted Setting [pdf]
- Stewart Grant (MSc 2018) → PhD at UCSD
- Inferring and Asserting Distributed Invariants [pdf]
- Adalberto Júnior (PhD 2018 Federal University of Pernambuco, co-supervised with Nelson Souto Rosa) → Postdoc at UBC/IBM
- Runtime Adaptation of Microservices [pdf]
- Peter Chen (MSc 2017) → Arista Networks
- Cross-platform Data Integrity and Confidentiality with Graduated Access Control [pdf]
- Wali Usmani (MSc 2017, co-supervised with Konstantin Beznosov) → TwoTallTotems
- "Not able to resist the urge" : Social Insider Attacks on Facebook [pdf]
- Keheliya Gallaba (MASc 2015 from ECE, co-supervised with Ali Mesbah) → PhD at McGill U.
- Characterizing and refactoring asynchronous JavaScript callbacks [pdf]
- Michael Phan-Ba (MSc 2015)
- A literature review of failure detection within the context of solving the problem of distributed consensus [pdf]
- Daniel Rozenberg (MSc 2015) → Google
- Qualitative Repository Analysis with RepoGrams [pdf]
Postdoctoral fellow and research associate alumni:
- Cleidson de Souza (Research Associate 2022-2023, co-supervised with Dongwook Yoon)
- Mohamad-Jaafar Nehme (Postdoc 2021, co-supervised with Chen Feng and Victoria Lemieux) → Huawei Research
- Adalberto R. Sampaio Junior (Postdoc 2021) → Huawei Research
- Yanyan Zhuang (Postdoc 2016, co-supervised with Justin Cappos) → Assistant Prof. at U. of Colorado, Colorado Springs
Undergraduate UBC/visiting alumni:
- Kuter Bors (Directed Studies Winter'25)
- Oliver Oxford (Honors thesis'25)
- Ryan Wang (Directed Studies Fall'24)
- Kuter Bors (Directed Studies Summer'24 term 1)
- Liu (Andrew) Lu (Directed Studies Summer'24 term 1)
- Emilie Ma (Directed Studies Winter'24)
- Armin Talaie (Directed Studies Winter'24)
- Ken Li (Directed Studies Fall'23, Winter'24)
- Leo Foord-Kelcey (COGS 402 Summer'23, Directed Studies Winter'23, Fall'22)
- Kim Dao (Directed Studies Winter'23)
- Emilie Ma (Directed Studies Winter'23 with Dongwook Yoon)
- Aanandi Sidharth (COGS 402 Winter'23)
- Eric Yan (Honors thesis'23, Directed studies Summer'22)
- Qiyu Zhou (Directed Studies Winter'23)
- Kenneth Averna (Directed Studies Fall'22, COGS 402 Summer'22)
- Patrick Lee (Directed Studies Fall'22, Directed Studies Winter'22, COGS 402 Summer'22)
- Jesse Wong (Directed studies Fall'22, co-supervised with Dongwook Yoon)
- Dhruv Khanna (Directed studies Summer'22)
- Sol Lee (Directed Studies'22, Summer'22)
- Yennis Ye (WLIUR'22)
- Konstantin Pandl (Visiting PhD student, Summer'22)
- Crystal Lee (Directed Studies'22)
- Ruchit Palrecha (Directed Studies'22)
- Alamjeet Singh (Directed Studies'21,'22)
- Naveen Sivasankar (Honors thesis'21; with Dongwook Yoon)
- Kadir Mert Barutçuoğlu (Directed Studies'21)
- Vita Chan (Directed Studies'21)
- Prayus Shrestha (Directed Studies'21)
- Florentina Simlinger (Directed Studies'21)
- Haley Li (Directed Studies'20, '21, USRA'21)
- Charlene Nicer (Directed Studies'20, '21x2)
- Ahmed Abdelmoneim (Honors thesis'21; with Aline Talhouk)
- Maximilian Was Damji (Honors thesis'21)
- Chris West (Honors thesis'21)
- Daisy Zhang (Directed Studies'20)
- Wonhu Choi (Directed Studies'20)
- Kalli Leung (Directed Studies'20; with Mathias Lécuyer)
- Julian Mentasti (Directed Studies'20)
- Aditya Chinchure (WLIUR'20, co-supervised with Aline Talhouk)
- Kalli Leung (USRA'20, co-supervised with Aline Talhouk)
- Haley Li (SURE'20)
- Daisy Zhang (SURE'20, co-supervised with Aline Talhouk)
- Stephen Ye (Visiting PhD student from Beihang University, 2018-2019)
- Chris Yoon (USRA'18, USRA'19)
- Matheus Stolet (Directed Studies'19, URA'19)
- Marlon Ou (Directed Studies'18, '19)
- Eric Semeniuc (Honors thesis'19)
- Yifan (Tom) Yang (Directed Studies'19)
- Lise Savard (Directed Studies'18)
- Heming Zhang (MITACS Globalink research intern'18)
- Vaastav Anand (WLIUR'18)
- Anny Gakhokidze (Directed Studies'18)
- Finn Hackett (Directed Studies'18, CPSC 490)
- Michael Hou (Directed Studies'18)
- Syed Umair (Directed Studies'18)
- Amy Zhu (USRA'18, Directed Studies'18)
- Brandon Zhang (SURE'17)
- SOSP SRC'17 winner
- Vincent Hui (USRA'16, Directed studies'16, '17)
- Syed Iqbal (USRA'17)
- Jamie Koerner (Directed Studies'17)
- James Liu (Directed Studies'17)
- Stewart Grant (USRA'16, SURE'15, Directed Studies)
- Hendrik Cech (DAAD'16)
- Haoran Yu (USRA'16)
- Graham St-Laurent (USRA'16, Directed Studies)
- Caroline Lemieux (USRA '14, '15, Directed Studies)
- Patty Wang (USRA'15)
- Albert Xing (USRA'14)
- Kenneth Shen (SURE'14)
- Perry Liu (USRA'14)
- Jodi Spacek (Directed Studies)
- Dennis Park (Directed Studies)
- Alex Crooks (Directed Studies)
- Max Erler (Directed Studies)
- Mike Fink (Directed Studies)
- Gurkaran (Gary) Poonia (Directed Studies)
- Alex Ristich (Directed Studies)
- Bob Yang (Honors thesis)
Undergraduate U. Washington alumni:
- Roykrong Sukkerd (Honors thesis)
- Jenny Abrahamson (MSc, Honors thesis)
- Google Anita Borg scholarship winner
- Andrew Davies
- Michael Sloan
- Yoong Woo Kim
- Zachary Stein
- Kevin Thai
- Timothy Vega (Honors thesis)
- Katherine Baker
- Vjekoslav Brajkovic
- Maxwell Forbes
- Allison Obourn (Honors thesis)
- Patrick Williams
- Tyler Oshiro
- Sean Ren
- Alper Sarikaya
- Linda Le
Teaching
I believe that the teaching of Computer Science, particularly systems courses, is well-suited to experiential learning, a process of learning that privileges student practice, experience, and reflection. In my teaching I use experiential learning as a base framework and adapt it to the course topic, the size of the class, and the available resources.
Winter 2023:
Introduction to Software Engineering 310. An undergraduate course introducing students to software engineering.
Fall 2022:
Introduction to Software Engineering 310. An undergraduate course introducing students to software engineering.
Winter 2022:
Distributed Systems 416. An undergraduate course covering core concepts in distributed systems.
Fall 2021:
Distributed Systems Abstractions 538B. A graduate course on abstractions in distributed systems.
Winter 2021:
Distributed Systems 416. An undergraduate course covering core concepts in distributed systems.
Fall 2020:
Distributed Systems Abstractions 538B. A graduate course on abstractions in distributed systems.
Winter 2019:
Topics in Distributed Systems 538B. A graduate course on topics in distributed systems.
Fall 2018:
Distributed Systems 416. An undergraduate course covering core concepts in distributed systems.
Winter 2018:
Distributed Systems
416. An undergraduate course covering core concepts in distributed
systems.
Fall 2017:
Computer Networks
527. A graduate course focusing on classic and contemporary
networks topics.
Winter 2017:
Distributed Systems
416. An undergraduate course covering core concepts in distributed
systems.
Fall 2016:
Distributed Systems
538B. A graduate course on distributed systems.
Distributed Systems 416. An undergraduate course covering core concepts in distributed systems.
Fall 2015:
Computer Networks 527. A graduate course focusing
on classic and contemporary networks topics.
Winter 2015:
Distributed Systems
538B. A graduate topics course covering classic papers in
distributed systems.
Winter 2014:
Comprehension and
Analysis of Large System 538B. A graduate, project-based, topics
course covering a broad range of material, from software engineering
to distributed systems.
Fall 2013:
Software
Construction 210. An undergraduate second-year course.
Service to my communities
I consider the peer review process a critical component of academic research. Because of the breadth of my research program, I am involved with several different research communities, including systems and software engineering. I contribute in service roles to as many of these communities as I can.
- Organizer:
- 2026: ACM Symposium on Cloud Computing (SoCC) PC co-chair, with Eric Lo
- 2022: ICSE Co-located events co-chair with Christine Julien
- 2020: EuroSys Shadow PC co-chair with Étienne Rivière, NSDI posters co-chair with Ravi Netravali
- 2019: ICSE Student Volunteers co-chair with Shane McIntosh
- 2017: HotOS General co-chair with Rachit Agarwal
- 2017: VISSOFT PC co-chair with Andrea Mocci
- 2015: Middleware Doctoral symposium chair
- Program committee member:
- 2026: ICSE, PLDI
- 2025: ATC heavy, ICSE NIER
- 2023: ICSE
- 2022: ASE, EuroSys light, VISSOFT, ICSE Workshops, ResilientFL workshop
- 2021: EuroSys light, VISSOFT
- 2020: NSDI light, ASE, HotCloud, VISSOFT
- 2019: ICDCS, VISSOFT
- 2018: ICDCS, ESEM, ESEC/FSE NIER, ISSTA Demos
- 2017: ISSRE, ESEM, ICSE NIER, ICSE SRC, ISSTA Demos
- 2016: ICSE, ESEM, ICSE Posters, VISSOFT NIER and Demos
- 2015: SRDS, ICSE Demos, VISSOFT NIER and Demos
- 2014: ICSE Posters
- 2013: SOSP Posters
- 2012: WikiSym
- 2011: WikiSym
- Steering committee member:
- 2023 - 2025: HotOS
- 2017 - 2022: VISSOFT
- Journal/conference boards:
- 2018 - 2023: TSE review board
- Reviewer:
- 2024: TOSEM, TSE
- 2019: TSE, IST, JSS
- 2018: TSE, JSS
- 2017: CHI, EuroSys, TOSEM
- 2016: TSE, JSEP, JSPE
- 2015: TSE, Elsevier ASE, ASE
- 2014: TSE, VLDB, Elsevier IST
- 2013: TSE, OSR, ASE
- 2012: TSE, TOOLS
- 2011: OOPSLA, NCA
- 2010: SigMetrics
- 2009: NSDI, WikiSym
Funding
I am fortunate to have my research and education efforts supported by the following generous organizations: NSERC, Amazon (AWS Automated Reasoning Group), Huawei, UBC Designing for People, UBC Data Science Institute, Cascadia Data Alliance, Aquanow, Microsoft, Microsoft Azure, IBM CAS, Shopify, Mitacs, Tasktop, NSF, UBC, Office of the Privacy Commissioner of Canada, Amazon, Peter Wall Institute.
Media coverage
I am always happy to chat with media to showcase research from my group or to discuss and explain recent technology trends.
- June 24, 2024. Our FSE 2024 paper was featured in an article published by thenewstack.io. What GitHub Pull Requests Reveal about Your Team’s Dev Habits. Our work documents developers' work practices from analysis of graphs formed by links between issues and pull requests on GitHub.
- November 4, 2021. An article that describes the work behind our CSCW 2021 paper on references in GitHub pull requests. The paper was awarded an impact recognition.
- November 17, 2020. Clement Fung gave an interview for the Data Skeptic podcast about our work on Sybil Attacks on Federated Learning (RAID 2020 pdf).
- November 5, 2020. Fred Hutch News Stories. New regional collaborations will accelerate innovation in data-intensive medical science. (highlights our LEAP project)
- Erlay: Efficient Transaction Relay for Bitcoin (CCS 2019 pdf)
- August 9, 2019. BitCoin Magazine. How the New Erlay Protocol Could Speed Up the Bitcoin Network
- July 27, 2019. Podcast interview on Advance Tech Podcast. Deep Dive Into Erlay
- June 3, 2019. Coinfomania. Why Erlay Protocol is a Big Deal for Bitcoin
- June 3, 2019. Forklog. Разработчики биткоина представили протокол Erlay для повышения пропускной способности сети
- June 3, 2019. Blockonomi. Full Nodes & Block Size: The Importance of Keeping Validation Costs Low in Bitcoin
- June 2, 2019. Coindesk.Maxwell, Wuille Co-Author Proposal for a Big Boost to Bitcoin’s Bandwidth
- Vulnerability & Blame: Making Sense of Unauthorized Access to Smartphones (CHI 2019 pdf)
- July 2019. Our study is featured on the Daily Show with Trevor Noah.
- June 2019. Bustle. Could Snooping On Your Partner's Phone End Your Relationship? A New Study Says Yes
- June 3, 2019. CBS. Yes, Snooping On Your Partner’s Phone Could End The Relationship, Study Finds
- May 30, 2019. Radio Canada. Would your relationship survive phone spying?
- May 30, 2019. Science Daily. Combing through someone's phone could lead to end of relationship -- or not
- Additional coverage in City News, Black Press Media, ABC 10, and others.
- January 3, 2018. The Abbotsford News. Bitcoin: From the computer to Abbotsford stores.
- January 22, 2017. Podcast interview on Snow Crash Radio. Week in review for January 22, 2017
- November 21, 2017. CBC BC Almanac Radio appearance. Cryptocurrency topics discussion.
- Characterizing Social Insider Attacks on Facebook (CHI 2017 pdf)
- January 27, 2017. CBC News.Beware! Friends, family, secretly snooping on your Facebook account
- Additional coverage in Vancouver Sun, The Times, Yahoo UK, Yahoo Canada, CBC Canada, CBC British Columbia, Metro News, The Province, Voice Online, Daily Mail, Hindustan Times, Daily Hive, Business Tech, and others.