| look | see | run | value |
| true | true | yes | 23 |
| true | true | no | 8 |
| true | false | yes | 37 |
| true | false | no | 56 |
| false | true | yes | 28 |
| false | true | no | 12 |
| false | false | yes | 18 |
| false | false | no | 22 |
- What is the resulting factor after eliminating run? (Hint: you do not sum out run as it is a decision variable).
- What is the optimal decision function for run?
| contaminated specimen | positive test | discard sample |
| true | true | yes |
| true | false | no |
| false | true | yes |
| false | false | no |
In a nuclear research submarine, a sensor measures the temperature of the reactor core. An alarm is triggered (A=true) if the sensor reading is abnormally high (S=true), indicating an overheating of the core (C=true). The alarm and/or the sensor can be defective (S_ok=false, A_ok=false) which can cause them to malfunction. The alarm system can be modelled by the following belief network (all variables are Boolean):
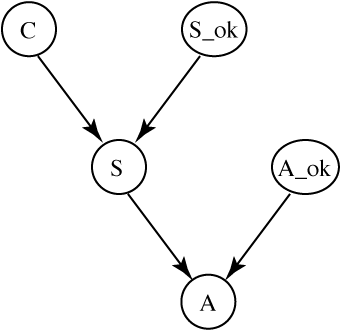
- Suppose we add a second, identical sensor to the system and trigger the alarm when either of the sensors reads a high temperature. The two sensors break and fail independently. Give the corresponding, extended belief network. (Draw the graph and specify any new conditional probabilities).
- When an alarm is observed, a decision is made whether to shut down the reactor. Shutting down the reactor has a cost cs associated with it (independent of whether the core was overheating), while not shutting down an overheated core incurs a cost cm much higher than cs. Draw the decision network modelling this decision problem for the original system (i.e., only one sensor). Specify any new tables that need to be defined (you should use the parameters cs and cm where appropriate in the tables). You can assume that the utility is the negative of cost.
- For the decision network in part (c), suppose you need to compute the optimal policy, and the value of the optimal policy using variable elimination. Show, for one legal elimination ordering, what variables are eliminated and what factors are created. [Just give the variables in the factors, not the tables of numbers.]
- How can the decision function(s) and its expected value be extracted from the elimination of part (d).
They are planning on building an intelligent tutoring system for teaching elementary physics (e.g., mechanics and electro-magnetism). One of the things that the system will need to do is to diagnose errors that a student may be making.
For each of the following, answer the explicit questions and use proper English. Answering parts not asked or giving more than one answer when only one is asked for will annoy the boss and result in reduced marks in the exam. The boss also doesn't like jargon, so please use straightforward English.
The boss has heard of consistency-based diagnosis, abductive diagnosis and belief networks, but wants to know what they involve in the context of building an intelligent tutoring system for teaching elementary physics.
- Explain what knowledge (about physics and about students) consistency-based diagnosis requires.
- Explain what knowledge (about physics and about students) abductive diagnosis requires.
- What is the main advantage of using abductive diagnosis over consistency-based diagnosis in this domain?
- What is the main advantage of consistency-based diagnosis over abductive diagnosis in this domain?
- Explain what knowledge (about physics and about students) a belief network model requires.
- What is the main advantage of using belief networks (over using abductive diagnosis or consistency-based diagnosis) in this domain?
- What is the main advantage of using abductive diagnosis or consistency-based diagnosis compared to using belief networks in this domain?
Suppose you are given the following scenario. There are four possible diseases a particular patient may have: p, q, r and s. p causes spots. q causes spots. Fever could be caused by one (or more) of q, r or s. The patient has spots and fever.
- Show how to represent this theory using Horn clauses.
- Show how to diagnose this patient using abduction. Show clearly the query and the resulting answer(s).
- Suppose also that p and s cannot occur together. Show how that changes your theory from part (a). Show how to diagnose the patient using abduction with the new theory. Show clearly the query and the resulting answer(s).